Businesses fear attacks by cybercriminals, and there are several ways the dark web can catch you. Malware is one of them. Studies show that the average cost of a malware attack could be around US$ 2.4 million. It is good to know about them, which will allow you to stay safe from them. We will start by discussing malware and the different types of malware, apart from learning how to prevent them.
What is malware?
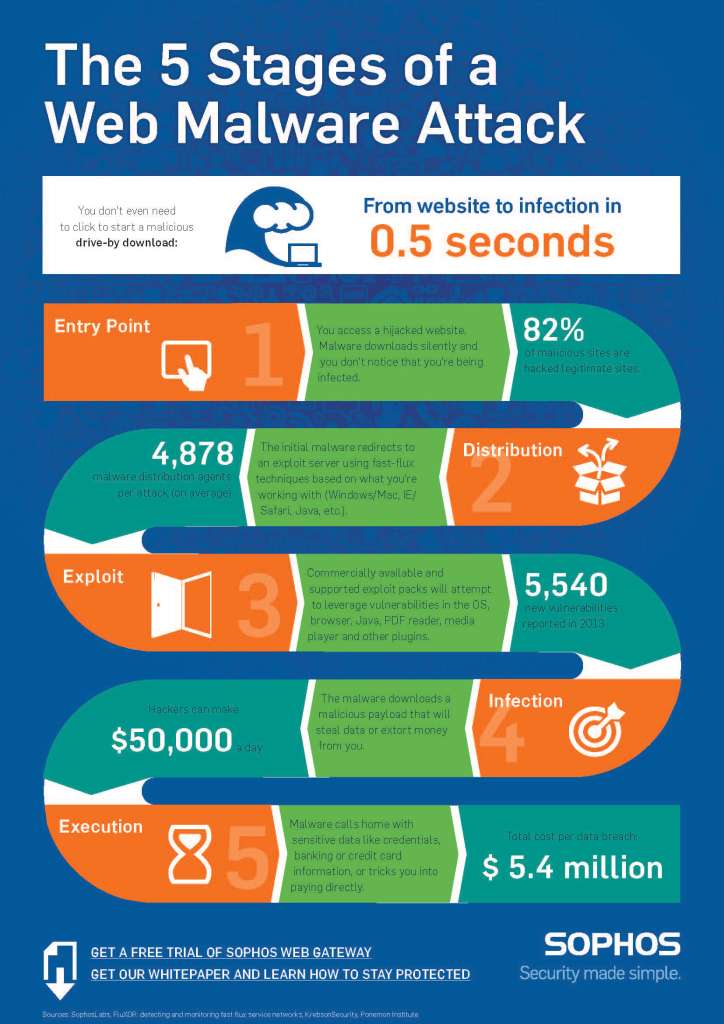
It is malicious software that can allow hackers to access your network for accessing sensitive information. It can hide within genuine applications to harm unknowing users. Let us learn more about the different types of malware.
Spyware
It can gather information from unsuspecting users secretly. This malware can spy on your behaviour with the device along with the information exchange done with it. It can operate through an app too.
Worms
They try to exploit the weaknesses in the operating system and can also replicate to attack other computers. They do not require any intervention to activate their malicious code. They can steal critical information or even delete files.
Viruses
Viruses can bring harm to a computer in various ways, viz. shutting your system, making ransomware, or DDoS attacks. It can replicate its own and spread the malicious code to other devices or reformat your drives or corrupt your data. They are distributed through downloads or email attachments.
Trojan Horse
Trojans look like valid programs but contain malicious code underneath. They are usually pushed through spammy sites or as email attachments. Of late, remote access trojans are used by hackers to take over your terminals remotely.
Ransomware
It infects networks and shows messages with a demand for a fee to be paid to ensure your systems can work again normally. The target business can be rendered inactive – wholly or partially until the amount is paid. They can be installed through websites or deceptive links in emails.
Fileless malware
It can already reside within your computer and uses legitimate software that is present on your computer. These attacks are usually made through scripts and executables. They are challenging to detect, and studies show that fileless malware attacks grew by around 256% in the first half of 2019.
Cryptomining
In this procedure, cybercriminals write malware that is made to run on other computers and devices. These resources are forced to do the mining for them. One of them is cryptojacking, where the processing power of the victim devices is exploited.
Adware
The adware tracks your online activity and uses unique algorithms to decide the ads shown to you. The data captured by the adware can be sold out to third parties without the user’s consent. It can also redirect to ad sites or even change your browser settings.
Keyloggers
It is like spyware that tracks your online activity. It can also track what the user is typing by recording the keyboard activity. Hackers can use it to capture your sensitive personal data and even financial credentials.
Botnet malware
Botnets are a network of affected devices. These compromised devices could be IoT devices, servers, etc., that hackers can use to launch coordinated attacks.
How to protect networks against malware
It would be best if you protected your networks against such malware attacks. It can be challenging, but you can take these necessary precautions.
Using an SSL certificate for your website
If you use an encrypted connection for your website, it will protect your users as their communication cannot be accessed by any third-party. You must install an SSL certificate that will help you to ensure that the visitors to your website need not bother about third-party having access to their information. It is more helpful if you are storing user data on your website.

(Source:https://www.newvisiondigital.co/blog/what-is-an-ssl-certificate-and-why-is-https-important)
Update all your systems
You must keep all the internal systems of your business up to date. There must be processes to alert the IT team whenever there is a new update for the software. If you are using a content management system, ensure that it is on the latest version. The website theme and plug-ins must also be updated.
Restrict access
You must restrict access to critical systems in the organization. Not everyone in the organization would need access to all parts of the network. Also, relevant people must use global password best practices to have access to the systems. The use of password managers must be encouraged too. It becomes necessary to undertake penetration testing periodically.
Use antivirus for safety.
Your networks must have a robust antivirus that will ensure that your underlying devices and networks are protected from malware and other attacks. It is also essential to keep the antivirus updated with the latest additions to the virus database.
Ring Fence, your employees
You must have strict protocols in place for those working from home or bringing their own devices. You may also introduce email signing certificates to encrypt the messages that go out. It is also essential to put in place email security mechanisms like SPF, DMARC, or DKIM. Regular training of employees on ways to prevent cyberattacks can also help.
Conclusion
Malware attacks can lead to the loss of sensitive data and result in a huge penalty and associated lawsuits. It is essential to protect your networks as well to prevent such attacks. You must also ensure that the communication with the visitor to your websites remains protected by installing an SSL certificate. We have also discussed other ways to prevent malware attacks.

